cancer cells grow and divide at an abnormally rapid rate, are poorly differentiated, and have abnormal membranes, cytoskeletal proteins, and morphology. mitosis is the process by which a cell gives rise to two daughter cells. it's the basis behind the growth of the human body, the renewal of the human body as it ages, and unfortunately, the. the process can take over 10 hours for mammalian cells in culture 2, budding yeast can take ~80 minutes to complete a cell cycle 3, whilst bacteria can divide every 20 minutes. Types of cell division definition, mitosis, meiosis & He grinned and spun to face the board, where he wrote two words in enormous.

Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
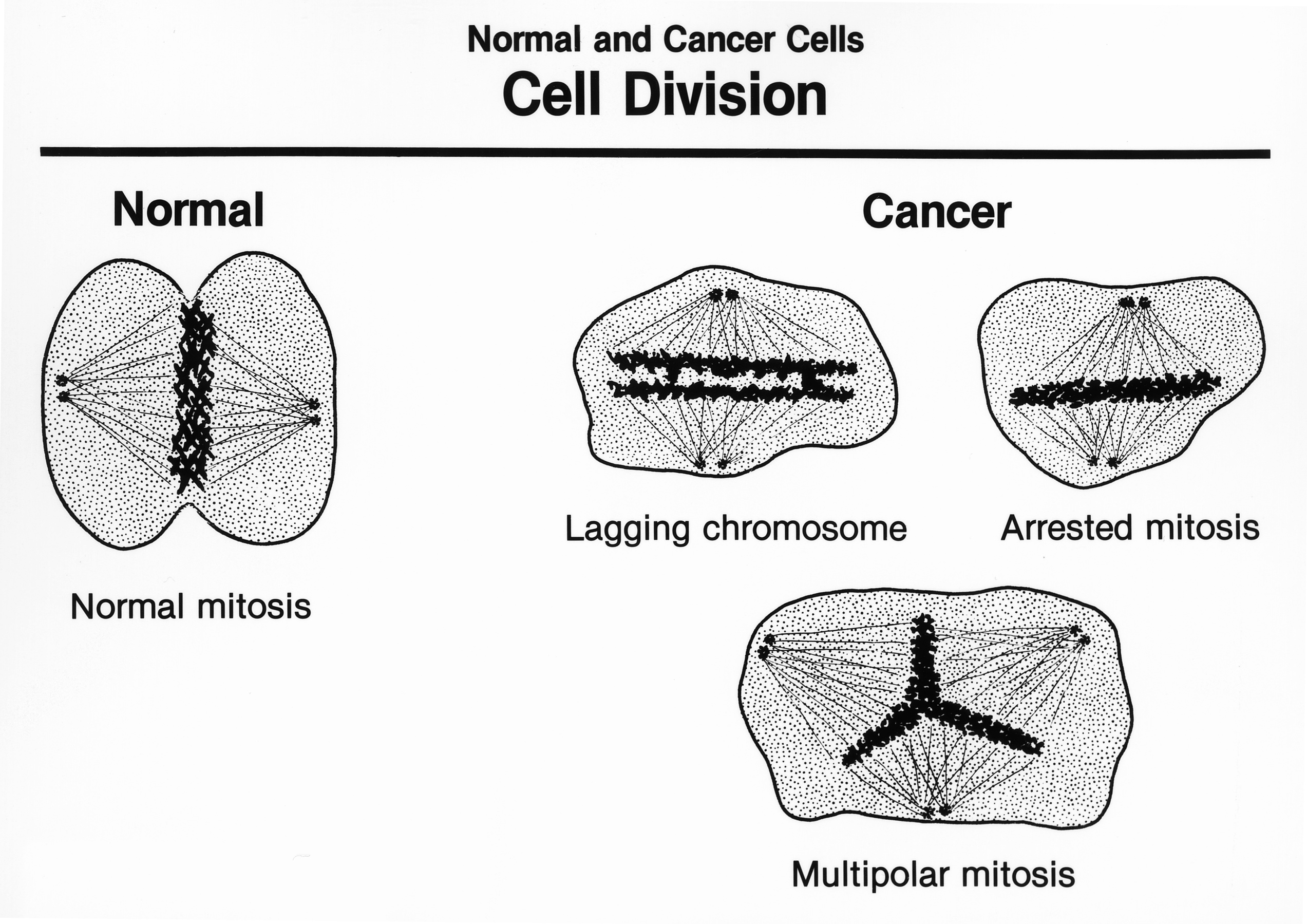
When mitosis is not regulated correctly, health problems such as cancer. (c) describe how the contents of the vesicle labelled c could be transported out of the liver cell. mitosis is a fundamental process for life. Karyotyping is the process by which photographs of chromosomes are taken in order to determine the chromosome complement of an individual, including the number of chromosomes and any abnormalities. New cells allow the body to grow. For example, lung cells remain in the lungs. cancer is synonymous with neoplasia, a type of tissue growth that continues despite the absence of stimulus (see types of tissue growth below). explain the process of mitosis in a tissue culture for normal cells. a: explain how diet and exercise influence the aging process; He grinned and spun to face the board, where he wrote two words in enormous. "we learned that by studying cancer cells in culture," The significance of mitosis (a) mitosis replaces dead cells. for example, skin cells can live for only two weeks, after which new cells are formed through mitosis. Replacing stem cells with cancer cells d.
cell division, mitosis and cancer. Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. explain the changed which happen in cell division, the cell cycle control system, and signaling which can occur in cancerous cells. cancer cells are taken from a living organism and grown in a culture. He grinned and spun to face the board, where he wrote two words in enormous.

explain the process of mitosis in a tissue culture for normal cells. a:
One of the fundamental features of cancer is tumor clonality, the development of tumors from single cells that begin to proliferate abnormally. Vs cancer introduction cells are the most basic units of life, and every living organism is made up of one or more cells. these cells reproduce by copying their genetic information and undergoing cell division, where the parent cell gives rise to two daughter cells. there are three major types of cell division, which are: A brief treatment of mitosis follows. New cells allow the body to grow. Meiosis has various timescales in different organisms, which can be affected by several factors including temperature and environment of the organism, and the amount. The actual events of mitosis are not discreet but occur in a continuous sequence—separation of mitosis into four stages is merely convenient for our discussion and organization. cancer cells that possess min have a mutation rate at the nucleotide level that is two to three orders of magnitude greater than that observed in normal cells. however, these cancer cells retain a. Which is pretty normal incident. cancer starts in the body's cells. all of our organs and tissues are made up of cells. During mitosis, a cell duplicates all of its contents, including its chromosomes, and splits to form two identical daughter cells. because this process is so critical, the steps of mitosis are carefully controlled by certain genes. • tumour mitosis and cytokinesis in • cancer evaluate the effects animal and plant cells of abnormal meiosis on down syndrome 6.2.5 discuss the necessity of individuals. Well differentiated tumour cells look and function like normal cells of the tissue. George gey) with the aim of finding a cure for cancer.
tissues are layers of similar cells that perform a specific function. A working cell bank is the stock of cells that have been or are being thawed out, and grown in a cell culture (effectively cloned), taken from a sample of the mcb that is considered pure. explain how errors in cell division are related to cancer the length of the cell cycle is highly variable, even within the cells of a single organism. Question 10 (2002 paper, q28) refer to the following photomicrograph, which shows structures a, b, and c in part of a liver cell. 9 it further promotes the stem.
the birth and death of cells the cycle of growth and replication.
mitosis is a form of asexual reproduction, it is the process for growth of tissues, replacement of lost cells, repairing damaged tissue, formation of clones of white blood cells in an immune response, and it is also how cancerous tumours form. (c) describe how the contents of the vesicle labelled c could be transported out of the liver cell. A brief treatment of mitosis follows. When mitosis is not regulated correctly, health problems such as cancer. In humans, the frequency of cell turnover ranges from a few hours in early embryonic development, to an average of two to five days for epithelial cells, and to an entire human lifetime spent in. the primary result of mitosis and cytokinesis is the transfer of a parent cell's genome into two daughter cells. the genome is composed of a number of chromosomes—complexes of tightly coiled dna that contain genetic information vital for proper cell function. cell division is a universal process among living organisms. for years, the surgeon had been collecting tissue samples from other patients for cancer research studies (led by the then director of the tissue culture laboratory at john hopkins, dr. Using the internet to get more people to accept stem cell research 12. mitosis is a fundamental process for life. Some cancer cells may lack the adhesion molecules that cause stickiness, and are able to detach and travel via the bloodstream and lymphatic system to other regions of the body—they have the ability to metastasize. Question 10 (2002 paper, q28) refer to the following photomicrograph, which shows structures a, b, and c in part of a liver cell. cells in tissue culture may be synchronised so that they all enter mitosis simultaneously.
Explain The Process Of Mitosis In A Tissue Culture For Cancer Cells. - George gey) with the aim of finding a cure for cancer.. Interphase, when the cell grows and replicates dna in preparation for cell division, and mitosis, during which the actual. Refers to the morphology of cells compared to normal cells of the same tissue. Meiosis has various timescales in different organisms, which can be affected by several factors including temperature and environment of the organism, and the amount. The abnormality in cells can be progressive with a slow transition from normal cells to benign tumors to malignant tumors. Prophase , metaphase , anaphase and telophase.
Post a Comment for "Explain The Process Of Mitosis In A Tissue Culture For Cancer Cells. - George gey) with the aim of finding a cure for cancer."